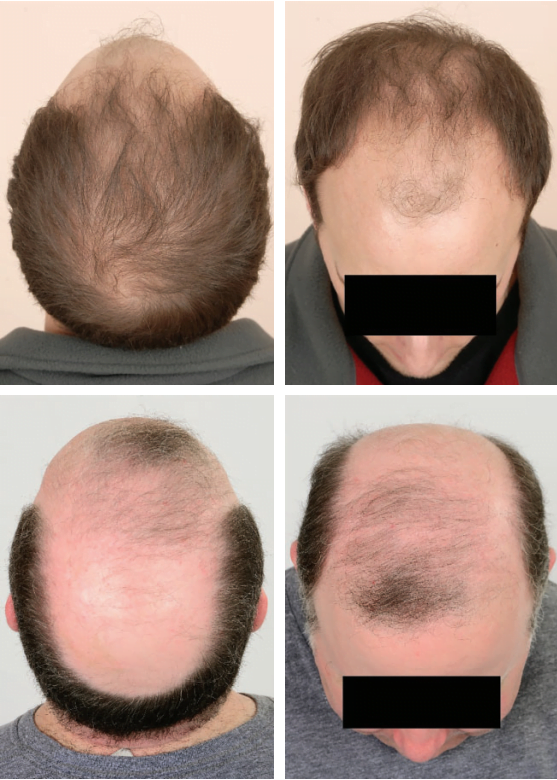
Understanding Hair Loss
Overview Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can target the scalp or the entire body and may be a temporary or enduring issue. It often stems from genetics, hormonal shifts, medical conditions, or simply aging. While hair loss is more prevalent in men, it can affect anyone.
Baldness Explained Excessive hair loss from the scalp is commonly referred to as baldness. Age-related hereditary hair loss is the usual culprit. People’s responses to hair loss vary: some embrace it, others disguise it with different styles or accessories, and some seek treatments to halt or reverse the process.
Consultation is Key Before deciding on a hair loss remedy, it’s crucial to discuss the underlying causes and potential treatments with a healthcare provider.
Symptoms Hair loss manifests in diverse forms, influenced by its cause. It might be abrupt or gradual, affecting just the scalp or the entire body.
Typical Signs of Hair Loss:
- Progressive Thinning: The most frequent pattern, especially with age. Men’s hairlines often recede, while women may notice a widening part.
- Patchy Spots: Some experience hair loss in circular areas, which might precede itchiness or discomfort.
- Sudden Loosening: Stressful events can trigger a temporary shedding of hair.
- Universal Hair Loss: Certain medical treatments, like chemotherapy, can cause widespread hair loss, which typically reverses post-treatment.
- Scalp Scaling: Indicative of ringworm, this can involve hair breakage and skin irritation.
When to Seek Medical Advice Persistent hair loss that causes distress or the desire for treatment should prompt a medical consultation. Early intervention is particularly advised for women noticing a receding hairline.
Causes Daily hair shedding is normal, but noticeable hair loss occurs when shed hair isn’t replaced.
Common Causes Include:
- Genetics: Androgenic alopecia, or pattern baldness, is a hereditary condition that develops predictably with age.
- Hormonal and Medical Factors: Hormonal changes or medical issues can lead to permanent or temporary hair loss.
- Medications: Some prescriptions can contribute to hair loss as a side effect.
For a comprehensive understanding and personalized advice, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Understanding the Impact of Radiation and Stress on Hair Loss
Radiation Treatments Undergoing radiation therapy, particularly on the head, can lead to hair changes. Regrowth may differ in texture or density.
Stressful Events Significant stress can cause noticeable hair thinning, usually temporary, as a delayed response to the event.
Hairstyling Choices Tight hairstyles and certain treatments can lead to traction alopecia, where hair loss might become permanent due to scarring.
Risk Enhancers Factors that may elevate the risk of hair loss include:
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of baldness.
- Aging: As you get older, the risk increases.
- Dramatic Weight Changes: Significant weight fluctuations.
- Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes and lupus.
- Stress Levels: High stress can impact hair health.
- Dietary Habits: Inadequate nutrition can affect hair growth.
Preventive Measures While genetic hair loss is inevitable, other types can be mitigated:
- Hair Care: Gentle handling, avoiding tight hairstyles, and minimizing heat treatments can reduce risk.
- Medication Review: Consult healthcare providers about potential hair loss side effects from medications.
- UV Protection: Shield hair from excessive sun exposure.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking has been linked to increased baldness risk.
- Chemotherapy Considerations: Discuss cooling caps with your oncologist to potentially prevent hair loss during treatment.
Content adapted from Mayo Clinic resources.