Diagnosis and Treatment of Achilles Tendon Rupture
When assessing an Achilles tendon rupture, your doctor will perform a physical examination to evaluate tenderness and swelling in your lower leg. If the tendon has completely ruptured, your doctor may be able to feel a gap.
During the exam, you might be asked to:
- Kneel on a chair or lie on your stomach with your feet hanging over the end of the exam table.
- Your calf muscle will be squeezed to check if your foot automatically flexes. If it doesn’t, a complete Achilles tendon rupture is likely.
To determine the extent of the injury (complete or partial), your doctor may order an ultrasound or MRI scan, which provides painless images of your body tissues.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Repair (Common in Younger, Active Individuals):
- Athletes and younger people often choose surgery for a completely ruptured Achilles tendon.
- Surgical management involves repairing the torn tendon.
- Nonsurgical Approach (Common in Older Individuals):
- Rest the tendon using crutches.
- Apply ice to the affected area.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Immobilize the ankle using a walking boot with heel wedges or a cast, with the foot flexed downward.
- Nonsurgical treatment avoids surgical risks like infection.
- Recent studies show favorable outcomes with early weight-bearing rehabilitation in nonsurgically treated cases.
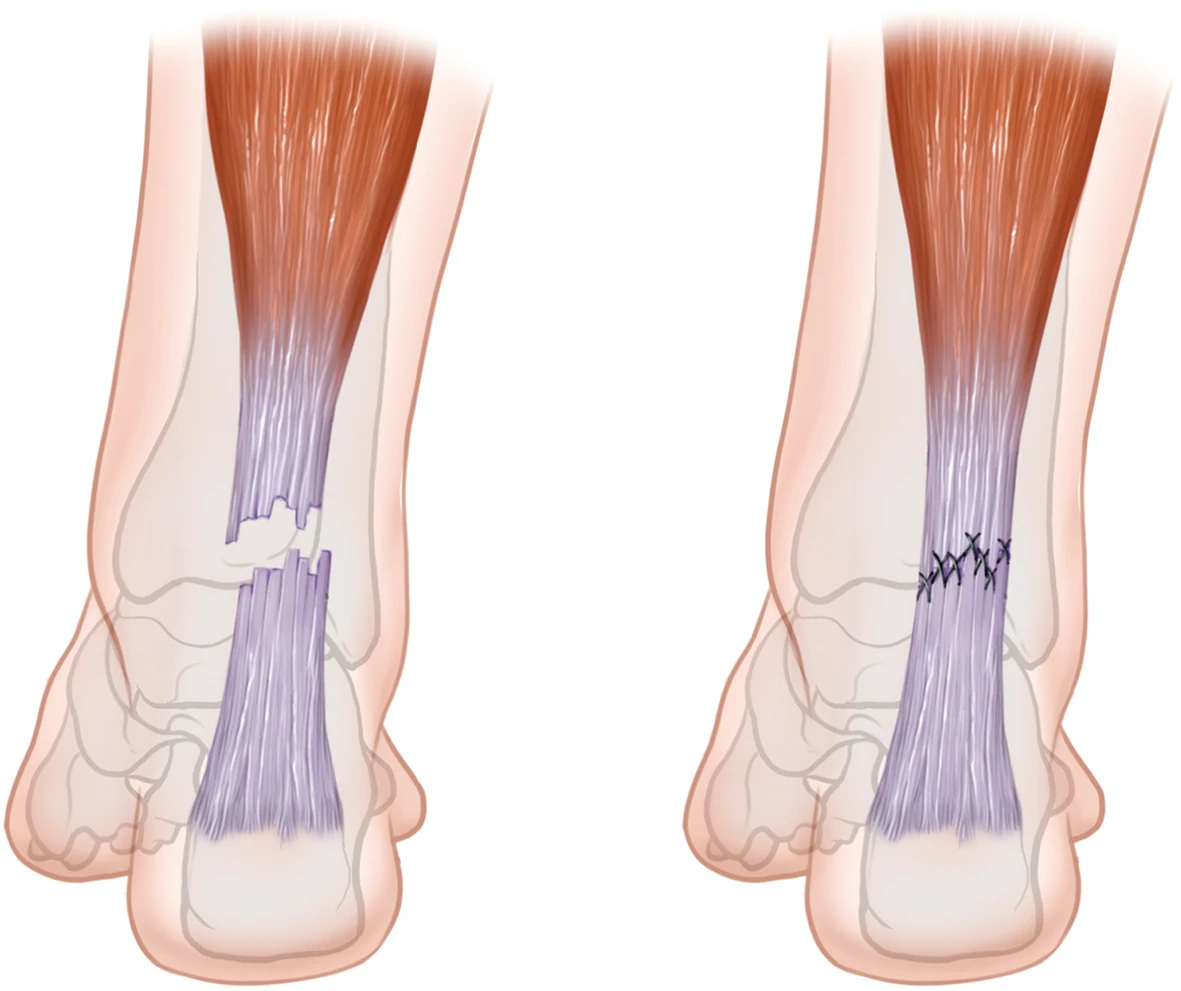
Surgical Repair and Rehabilitation for Achilles Tendon Rupture
Surgery:
- The surgical procedure typically involves making an incision in the back of your lower leg and stitching the torn tendon together.
- Depending on the condition of the torn tissue, the repair may be reinforced with other tendons.
- Complications can include infection and nerve damage.
- Minimally invasive procedures reduce infection rates compared to open procedures.
Rehabilitation:
- After either treatment (surgical or nonsurgical), you’ll undergo physical therapy exercises to strengthen your leg muscles and Achilles tendon.
- Most people return to their former activity level within four to six months.
- Continuing strength and stability training is crucial, as some issues can persist for up to a year.
- Functional rehabilitation focuses on coordinating body movements to restore your highest performance level, whether as an athlete or in daily life.
- A review study suggests that functional rehabilitation can yield similar outcomes to surgery, but further research is needed.
- Rehabilitation trends are moving toward earlier and faster progress, with ongoing studies in this area.
Preparing for Your Appointment:
- Seek immediate treatment at a hospital’s emergency department if you suspect an Achilles tendon rupture.
- Consult doctors specializing in sports medicine or orthopedic surgery.
- Prepare by:
- Describing symptoms and injury details.
- Providing information about past medical problems.
- Listing medications and dietary supplements (including doses).
- Formulating questions for the doctor.
What to Expect from Your Doctor:
- The doctor may inquire about:
- How the injury occurred.
- Whether you felt or heard a popping or snapping sound during the incident.
- Your ability to stand on tiptoe on the affected foot.